by Danielle Rothschild & José Valentino Ruiz, Ph.D.
Table of Contents
Abstract
This editorial examines the evolution, impact, and practical applications of orchestral fusion—the integration of live orchestras, digital orchestration tools, and classical instrumentation within mainstream music. Tracing its historical development from classical traditions to jazz, film scores, and contemporary popular music, it explores how artists like Laufey, Cody Fry, and Elton John utilize orchestration to enhance emotional depth and sonic richness. The discussion highlights the financial, logistical, and technical challenges of working with live orchestras versus synthesized alternatives, addressing how artists and producers navigate these constraints through hybrid approaches. Additionally, the editorial explores pedagogical strategies for integrating orchestral fusion into music education, emphasizing its value in bridging classical and contemporary styles.
Keywords: orchestral fusion, mainstream music, classical integration, music production, contemporary orchestration, music education, live performance challenges
The Evolution and Impact of Orchestral Fusion in Mainstream Music
Orchestral fusion in mainstream music has evolved from Western classical traditions to become an integral part of popular culture. Initially associated with composers like Mozart and Beethoven, orchestration expanded beyond classical music in the 1920s jazz era, with artists like Duke Ellington incorporating symphonic elements. This trend continued in 1930s film scores, where composers such as Max Steiner and Bernard Herrmann pioneered orchestral scoring in Hollywood (Wilson, 2022). By the 1960s, artists like The Beatles and Elton John embraced orchestral fusion, laying the groundwork for its continued presence in contemporary music. Today, artists such as Laufey, Cody Fry, and Elton John showcase its modern applications, using orchestration to enhance live performances, recordings, and cross-genre collaborations.
The increasing popularity of orchestral fusion stems from its emotional depth, grandeur in live performances, and versatility across genres. Many artists employ text painting, where orchestral elements mirror lyrical themes, intensifying emotional impact. Technological advancements—such as MIDI and digital orchestration tools—have made orchestral sounds more accessible, though the authenticity of live orchestration remains unparalleled. However, financial and logistical challenges persist, as hiring live orchestras and coordinating large-scale productions can be cost-prohibitive (Budanceva et al., 2022; Flanagan, 2012). Artists often turn to grants, crowdfunding, or hybrid orchestration approaches to balance cost and quality. As classical music evolves and technology advances, orchestral fusion is expected to expand further, reinforcing its enduring influence in contemporary music and media.
Economic and Logistical Considerations of Orchestral Fusion
The decision to use live orchestras versus synthesized orchestration in music production carries significant financial and artistic implications. Recording with a live orchestra requires substantial funding, with costs influenced by location, ensemble size, and session length. European orchestras often benefit from greater financial support, making them more cost-effective than their U.S. counterparts (Budanceva et al., 2022; Flanagan, 2012). Touring with an orchestra presents additional expenses, including travel, accommodations, and equipment logistics, making it far more costly than using synthesized orchestration.
While digital orchestration provides a budget-friendly alternative, it often lacks the authenticity and immersive depth of live performances. Though premium sample libraries can offer higher-quality sound, they remain a compromise compared to live orchestras. Many artists adopt a hybrid approach, blending live and digital elements to balance cost efficiency with sonic richness (Ruiz et al., 2020). Despite advances in digital orchestration, the depth and expressive nuance of a live orchestra continue to make it the gold standard for an unparalleled musical experience.
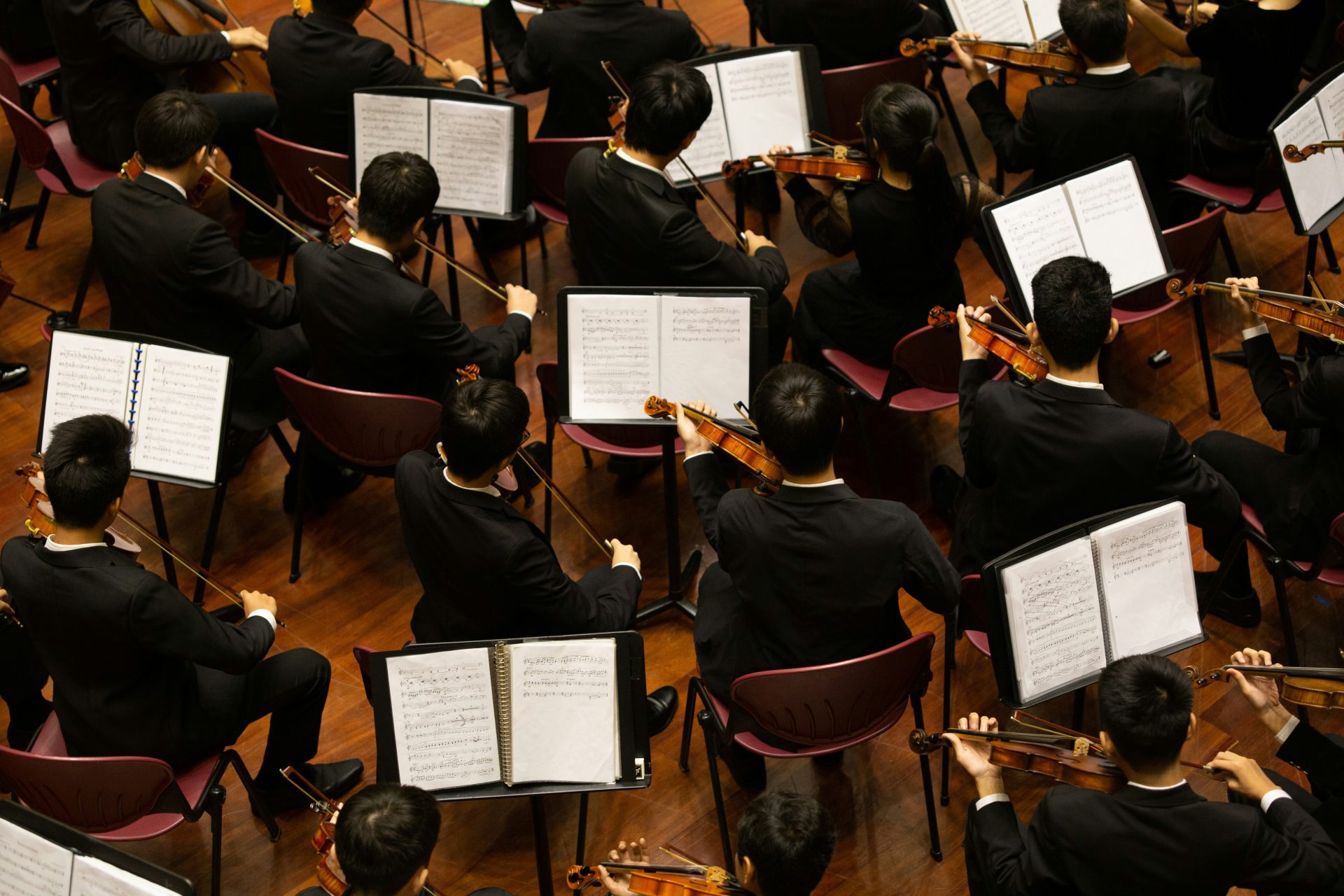

Challenges and Adaptation in Orchestral Fusion
Orchestral fusion enhances artistic expression and emotional depth, bridging classical instrumentation with contemporary music to create rich, layered textures. However, incorporating orchestral elements presents notable challenges. Many artists lack the technical expertise to compose and arrange for a full orchestra, requiring collaboration with skilled orchestrators. Additionally, financial and logistical constraints—such as hiring musicians, securing recording spaces, and managing large-scale productions—make live orchestration particularly difficult for independent artists.
Beyond financial and technical hurdles, artists must also navigate:
- Balancing Orchestration with Modern Production – Ensuring orchestral elements enhance rather than overshadow contemporary music.
- Audience Accessibility & Marketability – Orchestral fusion, while artistically compelling, may not always align with mainstream commercial trends.
- Performance & Touring Logistics – Adapting orchestral compositions for live settings requires venue accommodations, conductor coordination, and ensemble synchronization.
Despite these obstacles, orchestral fusion remains a powerful tool for artistic innovation, allowing musicians to elevate their compositions and forge deeper connections with audiences.
Pedagogical Approaches for Teaching Orchestral Fusion in Music Education
Integrating orchestral fusion into music education offers students a comprehensive understanding of both classical and contemporary music. Educators can introduce the concept by tracing its historical evolution and demonstrating its relevance through modern artists who incorporate orchestral elements into popular music. Using film scores, pop, and jazz as examples, students can explore how classical techniques from composers like Mozart and Beethoven remain integral to contemporary genres.
A curriculum that encourages hands-on learning can deepen students’ engagement with orchestral fusion. Assignments that incorporate orchestration in composition and arrangement projects allow students to experiment with layered textures and instrumentation. Teaching orchestration skills across multiple genres ensures that students understand how orchestral instruments can enhance different musical styles. Additionally, exposure to live or digital orchestral elements through performance opportunities fosters practical application and artistic creativity.
Analyzing modern songs that utilize orchestral elements helps students recognize arrangement techniques and production methods in contemporary music. Listening exercises can sharpen their ability to identify orchestral textures, while composition projects encourage them to integrate classical instrumentation into their own work. Emphasizing versatility and adaptability prepares students for diverse careers in music, ensuring they can seamlessly blend classical and modern techniques in their creative endeavors. All in all, embedding orchestral fusion into music education equips students with the skills to navigate an evolving industry while fostering a deeper appreciation for the role of orchestral music in contemporary settings.
Practical Strategies for Orchestral Fusion in Music Production
Successfully integrating orchestral fusion into music production requires technical proficiency, creative collaboration, and strategic industry adaptation. Producers must develop expertise in both digital tools and traditional orchestration techniques, mastering MIDI software, sample libraries, and DAWs to seamlessly blend orchestral and contemporary elements. Understanding orchestration, instrumentation, and dynamics is crucial for achieving authenticity, and collaborating with experienced orchestrators can bridge gaps in knowledge. However, working with live orchestras presents financial and logistical challenges, including musician fees, recording spaces, and production coordination. To manage costs, producers can explore grants, sponsorships, or hybrid approaches that balance live and digital elements for a full, dynamic sound.
Beyond technical skills, collaboration and industry awareness are essential for executing successful orchestral fusion projects. Networking with orchestrators, composers, and sound engineers enhances production quality, while staying informed on emerging trends in film scoring, video game music, and symphonic pop ensures continued relevance in a competitive industry. As technology advances and audiences increasingly embrace orchestral fusion, its influence in mainstream music will continue to expand—redefining creative expression and deepening audience engagement across genres. By mastering both the artistic and logistical aspects of orchestration, producers can effectively integrate orchestral elements into their music, fostering adaptability and innovation within the modern music industry.
Concluding Thoughts
The fusion of orchestral elements with mainstream music is a dynamic trend reshaping both the industry and music education. Beyond enriching artistic expression and emotional depth, it creates valuable pedagogical and professional opportunities. For educators, it bridges classical training with contemporary interests, expanding students’ musical understanding. For producers, it underscores the need for versatility and collaboration in overcoming financial, technical, and logistical challenges. As technology makes orchestral sounds more accessible and audiences increasingly embrace this fusion, its role in mainstream music will continue to grow, unlocking new possibilities for creative expression and engagement.
References
Budanceva, J., Soida, S., & Sondore, L. (2022). Opportunities for the Development of International Cooperation for Professional Orchestras. Economics and Culture, 19(1), 108-120.
Flanagan, R. J. (2012). The perilous life of symphony orchestras: Artistic triumphs and economic challenges. Yale University Press.
Ruiz, J. V., Cooper, P. K., & Muhammed, J. N. (2020). Can they hear a difference? Professional digital composition and the ability of music students to discriminate deep-sampled vs. acoustic instrumental performance recordings. Journal of Popular Music Education, 4(1), 81-99.
Wilson, S. (2022). The Sound of Cinema: Hollywood Film Music from the Silents to the Present. McFarland.



Leave A Comment